
High power dissipation will increase the copper wire temperature and the resistance as discussed Note 11.\): The magnetic field of a bar magnet, illustrating field lines.
#FLUX DENSITY CALCULATOR DRIVER#
Note 18: If the coil is driven by an AC driver such as the TS250, the RMS power dissipation is calculated using the user input (peak) current to calculate the RMS current and then calculate the RMS power. High power dissipation will increase the copper wire temperature and the resistance as discussed in Note 11. Note 17: This is the calculated coil power dissipation (in watts) for the DC current case. Therefore this is the minimum capacitor voltage rating. This is the peak voltage across the capacitor. Note 16: At resonant the voltage across the capacitor may be very large. It is calculated using the coil inductance and the user input frequency.
#FLUX DENSITY CALCULATOR SERIES#
Click here for more information about series resonant magnetic coil. The coil impedance is reduced or canceled using this series resonant capacitor (Figure 5). Note 15: This is the capacitance needed to form an LC resonant tank. Note higher voltage is need for AC waveform using the an amplifier driver such as the TS250, because resistance increase rapidly at higher frequency. As resistance is increase at hot, higher voltage is needed. Note DC resistance is calculated at room temperature. Note 14: This is the minimum voltage needed to drive the coil. It is calculated using inductance, frequency, and resistance. Note 12: Coil inductance in micro- Henry (uH). Resistance is further increase at higher temperature. Note 9: Calculated magnetic field at a distance from the coil center. A practical compact factor range is 0.88 to 1.0. This is the most tightly wound with no space wasted. However, practical wounding is shown in Figure 4. If the coil is wound such that the distance between two copper layers is equal to the diameter (Figure 3), the compact factor is equal 1.0. Note 8: Enter the coil winding density compact factor. Note 7: Enter the core relative permeability constant, k. Another example, a distance of 25mm means the magnetic field is calculated 10mm outside of the coil (30mm/2+10mm = 25mm). For example, if the coil bobbin width is 30mm, a distance of 15mm is at the coil edge. Enter zero for the magnetic at the center of the coil/solenoid. Note 6: The calculated magnetic at a distance from the center of the coil, see Figure 2. For DC, just leave the default 1kHz and use the DC parameters calculated below. Note 5: Enter the solenoid/coil operation frequency (sinewave). If the current is AC, this is the peak current. Note 3: Enter the number of turns in the coil or solenoid. Use Table 1 to enter the bare copper wire diameter.

This diameter is used to calculate the resistance more accurately. Once the brightness temperatures are known, it becomes possible to calculate the flux density received at the Earth from a given planet, corrected for the. Table 2: Copper wire diameter WITHOUT coated insulation. Use Table 1 to enter the copper wire diameter. Table 1: Copper wire diameter with coated insulation. It can be thought of as the density of the magnetic field lines - the closer they are together, the higher the magnetic flux density. It is also sometimes known as 'magnetic induction' or simply 'magnetic field'. The coil width is same as the bobbin inner width. Magnetic flux density is the amount of magnetic flux per unit area of a section that is perpendicular to the direction of flux.
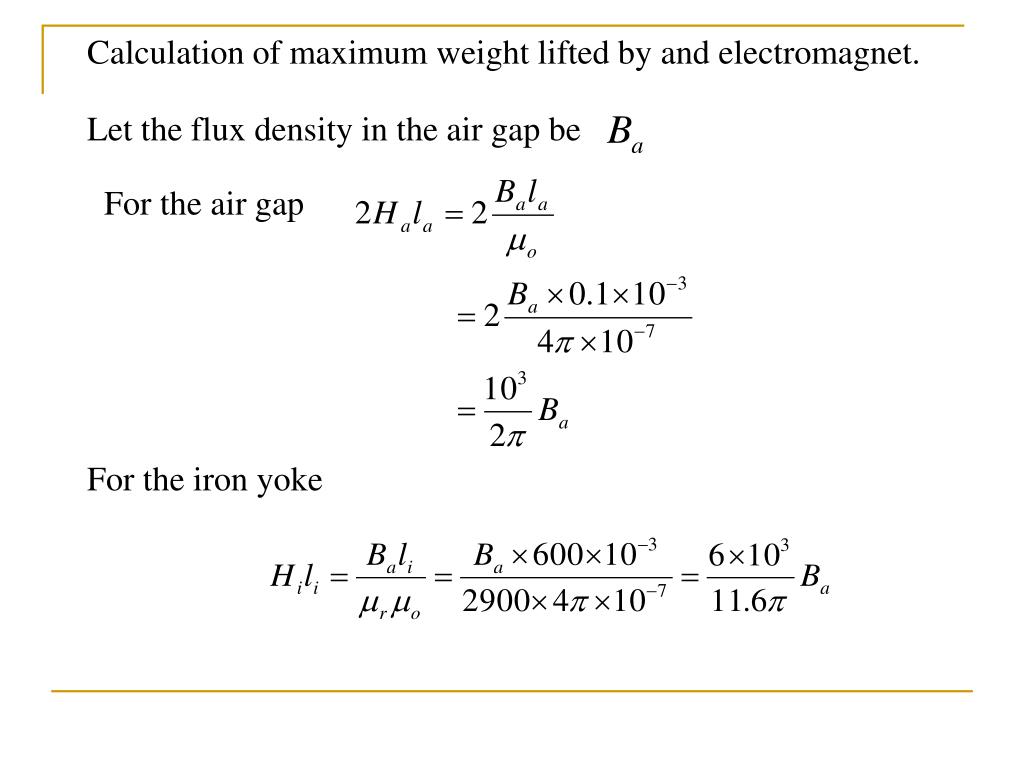
Note 2: Enter the length of the solenoid or coil. Copper inner radius must be larger than bobbin inner radius.

Note the copper inner radius is not same as the bobbin inner radius. Note1 : Coil copper inner radius from the center to the first layer of copper.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
